Psychological Laboratory, Harvard University
- Location
- Cambridge (MA)
VL Images
Source
Münsterberg, Hugo.
1893.
Psychological Laboratory of Harvard University.
Cambridge, Mass.: University Press of Cambridge, Mass..
Book
Associated Journals
Harvard Psychological Studies
Related records
Psychological Laboratory, Harvard University.
Cambridge (MA).
Anonymous.
1892.
Harvard Psychological Laboratory in Dane Hall: Interior of a Laboratory Room.
Photography
Anonymous.
1892.
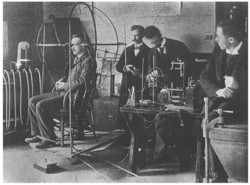
Harvard Psychological Laboratory in Dane Hall: Interior of a Laboratory Room (Chain Reaction Experiment).
Photography
Anonymous.
1892.
Harvard Psychological Laboratory in Dane Hall: Instruments for Experiments on Sight.
Photography
VL People

Hugo Münsterberg
head 1863 - 1916Herbert Nichols
assistantVL Sites
- Keywords
- Laboratory
- Technical instruments
- Objects for Anatomical and Physiological Demonstrations of the Physical Basis of Mental Life
- - Large wire model, showing the fibres and the cerebral masses. After Aeby, by Buechi, Bern
- - Large clastic model, showing the course of the nerve-fibres throughout the encephalic mass. After Luys, by Auzoux, Paris
- - Natural sized clastic model. showing the nerve-fibres on one hemisphere, and the cerebral ganglion masses on the other. After Luys, by Auzoux, Paris
- - Natural sized clastic model. By Bock-Steger, Leipzig
- - Large model, showing the convolutions. By Talrich, Paris
- - Largo model, showing horizontal section. By Talricht, Paris
- - Large model, seen from below. By Tairich, Paris
- - Large model of corpus callosum, seen from below. By Talrich, Paris
- - Large model, showing median section. By Talrich, Paris
- - Large clastic model of cerebellum and spinal cord. By Auzoux, Paris
- Vertical section of head. By Bock-Steger, Leipzig
- - Model of the head of adult male, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Model of the head of middle-aged female, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Model of the head of an aged man, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Model of the head of elderly female, insane, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Set of fourteen wax models, showing the development of the foetal brain. After Ecker, by Ziegler, Freiburg
- - Model of the head of a seven months’ foetus, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Model of the head of a child six months old, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Model of the head of a girl, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Collection of human brains in alcohol.
- - Collection of charts, showing sections of the brain, and forty-eight stereoscopic views of the central nervous system. After Debierre and Donmer, by Alcan, Paris
- - Set of eight wax models, showing the phylogenic development of the brain. After Wiedersheim, by Ziegler, Freiburg
- - Model of the head of chimpanzee, brain exposed on the side. By Casciani, Dublin
- - Model of the head of orang-utang brain exposed on the side. By Casciaui Dublin
- - Collection of sheep brains in alcohol
- - Collection of charts showing development of brain, from gymnotus to mammal
- - Half skull, with the seven first cerebral nerves in wax. By Tramond, Paris
- - Large clastic model of eye, divided by a vertical section. By Auzoux, Paris
- - Large clastic model of eye, showing muscles, nerves, vessels, etc. By Auzoux, Paris
- - Clastic model of human eye. By Bock-Steger, Leipzig
- - Small model of entire eye. By Browning, London
- - Set of nine wax models of the eye, showing the embryological development of the vertebrate eye. After Manz, by Ziegler, Freiburg
- - Standard eyes for anthropological comparison. After Galton. by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- Large clastic model of the ear, showing the internal, middle, and external ear. By Auzoux, Paris
- Large clastic model of the ear, showing especially the internal ear. By Brendel, Berlin
- Large collection of histological preparations for microscopical study of brain, sense-organs, nerves, and muscles. By Bourgogne, Paris; Queen, Philadelphia; Kloenne and Müller, Berlin, etc.
- here
- - Artificial eve, consisting of glass water-tank, lenses, etc. After Kuehne, by Jung, Heidelberg
- - Thread model, representing rays of light, and demonstrating effects of astigmatism. After Knapp. by Meyrowitz, New York
- Phakoscope, for demonstrating accommodation of lens. After Helmholtz, by Sittel, Heidelberg
- - Ophthalmotrope, demonstrating movements of the eye, and action of the different muscles which produce them. After Ruete, by Kohl, Chenmnitz
- - Model showing mechanism of the drum and bones of the ear. After Helmholtz, by Jung, Heidelberg
- Apparatus for Studying the Sensations: A. Hearing
- - The harmonical, furnishing 24 over-tones of C (66) and the first 16 of c (132). After Ellis, by Moore, London
- - One large tuning-fork, giving from 32 to 48 vibrations. By Koenig, Paris
- Set of twelve tuning-forks, with resonance-boxes, Ut2 Ut3, Mi3, Sol3, La3, Ut4, Mi4, Sol4, seventh harmonic of Ut2, Ut5, Re5, Mi5. By Koenig, Paris
- One extra Ut4 tuning-fork and one Ut4 + four vibrations, with resonance-boxes. By Koenig, Paris
- Five tuning-forks, with resonators, tuned to the characteristic notes of the vowels. After Helmholtz, by Koenig, Paris
- - Bow for vibrating tuning-forks. By Queen, Philadelphia
- Series of ten resonators. After Helmholtz, by Koenig, Paris
- - Series of twenty-two steel cylinders, giving notes from Ut7 to Ut10 by stroke of steel hammer. By Koenig, Paris
- Apparatus for testing the appreciation of difference in musical pitch. After Galton, by Camb. Scient. lnstr. Co.
- - Large bellows, with regulator and wind-chest for twelve pipes. By Koenig, Paris
- - Nine open wooden pipes, from Ut2 to Ut3, to be used with the organ-bellows. The Ut2 duplicated. By Koenig, Paris
- - Eight stopped pipes, giving the scale from Ut3 to Ut4. By Koenig, Paris
- - Apparatus for studying the non—musical intervals of sounds between 128 and 256 vibrations (Tonmesser). By Appunn, Hanau
- - Apparatus for studying the non—musical intervals of sounds between 256 and 512 vibrations. By Appunn, Hanau
- Revolving mirror, manometric capsule, etc., for analyzing manometric flames. By Koenig, Paris
- - Whistle for determining highest limit of sound, after Galton. By Koenig, Paris
- Differential sonometer, with weights. After Marloye, by Koenig, Paris
- Toothed wheel. After Savart, by Queen, Philadelphia
- - Siren and toothed wheels, giving the same notes, with centrifugal machine. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- some
- one
- - Snappers for giving different qualities of short noises, three telephones, pistols, etc.
- - Large electric phonometer, producing noises of various intensities. After Münsterberg. By Elbs, Freiburg.
- - Small phonometer. Made in the Laboratory
- - Two large boxes for tuning-forks impervious to sound, with ear appliances, etc. After Gilman, made in Cambridge
- Apparatus for Studying the Sensations: B. Sight
- Large color-mixer, with horizontal rotating disks, connected with foot-machine. Six dozen colored-paper disks. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- Apparatus for color-sense of the eccentric parts of retina, to be attached to Hering’s foot-machine. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- - Color-mixer, adjustable under rotation. After Pillsbury, by Bradley, Springfield.
- Large color-mixer for four disks, two upon each spindle. After Wundt, by Krille, Leipzig
- Set of color-disks, 60 ctm. in diameter. By Krille, Leipzig
- - Color-mixer. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- here
- Newton's disk, 80 ctm. in diameter. By Queen, Philadelphia
- Apparatus for mixing colors by mirrors and colored glasses. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- Apparatus for mixing colors by the combination of colored gelatine papers. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Three boxes for mixing colors by reflection. Made in the Laboratory
- Simultaneous contrast apparatus, with two prisms for binocular or monocular investigation. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- Simultaneous contrast apparatus, with colored glasses. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- - Instrument for the recombination of parts of the solar spectrum. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Instruments for successive contrast, irradiation, etc. By Kohl, Chernnitz
- Apparatus for color after-images. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- Chromatoskiameter. After Holmgren, by Rose, Upsala
- Apparatus for diagnosing color-blindness. After Hering, by Rothe, Prag
- Apparatus for appreciation of color. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Apparatus for testing simulated blindness. After Snellen, by Meyrowitz, New York
- - Nachet’s adjustable trial-frame. By Meyrowitz, New York
- Two perimeters. After Landholt and Priestley Smith, by Meyrowitz, New York
- - Two hundred and fifty perimeter charts. By Meyrowitz, New York
- Apparatus for testing keenness of eyesight. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co. (1892)
- - Spectroscope. After Vogel, by Schmidt and Haensch, Berlin
- Large glass prism, 15 x 10 ctm. By Queen, Philadelphia (1892)
- Two smaller mounted prisms. By Duboscq, Paris
- here
- Excelsior lantern. By Queen, Philadelphia
- Magic lantern.
- Gorham's kaleidoscope top. By Griffin, London
- Micrometric shutter for studying minute fields of color. After Münsterberg. By Elbs, Freiburg
- - Magnifying mirror. By Lloyd, Boston
- - Set of Geissler tubes
- Thirty plates colored glass. By Redding, Baird, and Co. Boston
- - Prismatic spectrum charts in frame. By Prang, Boston
- Apparatus for Studying the Sensations: C. Dermal and Muscular Sensations
- - Kinesimeter. After Hall, by Pfeifer, Baltimore
- - Tube for hot and cold spots
- - Six aesthesiometric compasses
- - Set of two hundred arrangements for studying number and extension of skin sensations. After Nichols; made in the Laboratory
- - Instrument for studying the fusion of touch sensations. After Krohn; made in Cambridge
- - Apparatus for testing appreciation of weight. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- Dynamometer for showing strength of hands. By Verdin, Paris
- - Salter’s dynamometer for showing strength of hands. By Camb. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Salter’s dynamometer for showing strength of arms. By Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- Apparatus for Studying the Higher Psychical Processes: A. Time Measurement of Mental Acts
- Kymograph. After Ludwig, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- Revolving drum. By Verdin, Paris
- - Two electric signals, one with tuning-fork attachment. After Deprez, by Verdin, Paris
- - Two tambours for giving signals upon revolving drum. After Marey, by Verdin, Paris
- - Two connected tambours. After Marey, by Verdin, Paris
- - Large demonstration-drums, etc. Made in Cambridge
- - Electrical tuning-fork of one hundred vibrations. By Koenig, Paris
- - Electrical tuning-fork of fifty vibrations. By Verdin, Paris
- - Electrical tuning-fork of ten vibrations. By Verdin, Paris
- - Registering tuning-fork of fifty vibrations, to be set in motion by a Bunsen aspirator. After Ewald, by Maier, Strassburg
- - Four simple writing tuning-forks. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Metronome, with electrical connection. After Kronecker, by Verdin, Paris
- - Hipp’s chronoscope, measuring one-thousandth part of a second. By Peyer, Favarger & Co., Neuchatel
- - Control hammer for Hipp’s chronoscope. After Wundt, by Krille, Leipzig
- - Pendulum instrument for giving rhythmical electric contacts and short optical impressions, and for controlling the chronoscope. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- Chronoscope measuring the hundredth part of a second, by registering the vibrations of a tuning-fork. After Ewald, by Maier, Strassburg
- - Clock measuring the hundredth part of a second, with spring and mechanical starter. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Stop-watch giving only fifths of a second. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Reaction-time pendulum. After GalLon, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Machine for measuring reaction-time by a falling rod. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Reaction-time instrument with vibrating arm and smoked slide. After Exner, by Heinitz, Wien
- - Large demonstration-chronoscope. After Wundt, by Krille, Leipzig
- - Flash-light instrument, with electric contact. After Bowditch, by Marie, Boston
- - Drop-window, for the sudden exposure of colors, numbers, etc. By Elbs, Freiburg
- - Touch-reaction instrument, with twenty different stimuli. By Elbs, Freiburg
- - Two telegraph keys, with sounder
- - Five simple telegraph keys
- - Electric key. After Ewald, by Maier, Strassburg
- - Electric key. After Dubois-Reymond, by Cambr. Scient. lnstr. Co.
- - Electric key, combined with writing signal. Made in the Laboratory
- - Reaction-key with fifty buttons. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Chain-reaction instrument for ten persons, each instrument provided with five electric keys and five frames. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Set of six hundred disks for the chain-reaction instrument. By Cooperat. Assoc., Cambridge, Mass.
- Apparatus for Studying the Higher Psychical Processes: B. Perception, Space, Time
- Instrument for investigating the power of the eye to compare lengths (Augenmassapparat). After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Instrument for the optical reproduction of given lengths. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Instrument for estimating the divisions of a line. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Instrument for estimating angular divisions. After Galton, by Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Wheatstone’s stereoscope, with slides. By Queen, Philadelpliia
- one
- Stereoscopic pictures. After Kroll, by Voss, Hamburg; and other sets
- - Twenty tin tubes, and pasteboard tubes for stereoscopic purposes
- Pseudoscope. After Ewald, by Maier, Strassburg
- - Pseudoscope. By Elliott, London
- - Two human concave masks, illustrating optical illusions
- - Apparatus for showing appreciation of distance by convergence. Made in the Laboratory
- - Haploscope. Made in the Laboratory
- - Set of charts, with optical illusions
- - Zoötrope
- - Stroboscopic rotating disk, with Geissler’s tube. After Poggendorff, by Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Artificial waterfall. After Bowditch; made in the Laboratory
- - Two large instruments for studying the muscle-sensations, tactual space, and the presentations of movement. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Apparatus for studying the perception of the position of the body. After Aubert; made in Cambridge
- - Apparatus for studying the localization of simultaneous equal or unequal sounds. After Münsterberg, by Elbs,Freiburg
- - Apparatus with electric contacts for studying the time-sense. After Schumann, by Diederichs, Goettingen
- - Sound-hammer for experiments on time-sense. By Krille, Leipzig
- - Metronome, with bell
- - Set of twenty-four instruments for studying space-sense in coordinated movements of both arms. After Bowditch, by Marie, Boston
- - Set of balls of the same weight, but of different sizes. By Marie, Boston
- Apparatus for Studying the Higher Psychical Processes: C. Association, Attention, Discrimination, Memory, Feelings, Emotions, Will, etc.
- - Material for studies in association (four hundred photographs, picture-books, large printed numbers, letters, words, etc.)
- - Eight sets of arrangements for studies in memory. Made in the Laboratory
- - Instrument for studies in association and memory. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Instrument for studying the complication of perceptions. After Wundt, by Krille, Leipzig
- - Instrument for the study of the attention, two simultaneous impressions being given to disparate senses. After A. H. Pierce ; made in the Laboratory
- - Instantaneous shutter for association experiments. By Elbs, Freiburg
- - Rotatory chair for the study of dizziness, etc. After Münsterberg, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Small instrument for studying the movements during the emotions. By Elbs, Freiburg
- - Large instrument for the study of aesthetic forms and proportions. After Münsterberg and Witmer, by Elbs, Freiburg
- - Six sets of arrangements for the study of aesthetic combinations of color. Made in the Laboratory
- - Cercle chromatique de Charles Henry
- - Ergograph. After Mosso, by Corino, Torino
- - Ponograph. After Mosso, by Verdin, Paris
- - Myograph. After Marey, by Verdin, Paris
- - Sphygmograph. After Marey, by Verdin, Paris
- - Instrument for registering the pulse of the two carotids at once. After Marey, by Verdin, Paris
- - Pneumograph. After Marey, by Verdin, Paris
- - Instrument for studying the time-relations of voluntary movements. After Loeb; made in the Laboratory
- - Apparatus for studying unconscious movements
- - Hypnoscope. After Luys
- Optical and Measuring Instruments
- - Two Heliostats. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Photometer. After Bunsen and Toepler,by Kohl, Chemnitz
- Microscope, with adjustment by graduated micrometer screw, Abbé condenser, iris diaphragm, cylinder diaphragms, double nose-piece, objectives, 2, 4, 7, 9, eye-pieces, i, iii, iv. By Leitz, Weimar
- Microscope. By Hart & Praz [Hartnack & Prazmowski], Paris
- - Small microscope. By Queen, Philadelphia
- - Photographic camera. By Lerchours, Paris
- here
- Cardboard and gelatine paper of various colors, two hundred sheets of colored paper, colored crayons, etc. By Milton Bradley Co., Springfield; Prang, Boston, etc.
- - Large and small finely graded thermometers, six ordinary thermometers
- - Three aërometers, measuring tubes for liquids, pipettes, etc.
- - Mathematical drawing instruments, protractors, etc.
- - Apothecary scale, with weights. By Whitall & Tatum, Boston
- - Balance scale, spring letter-balance, etc. By Fairbanks, St. Johnsbury
- - Two sets of brass weights. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Instrument for showing the variations of error from the average. After Bowditch, by Marie, Boston
- Electrical Apparatus
- - Eighteen Leclanche cells (Gonda)
- - Three Grenet cells
- - Sixteen Bunsen cells
- - Six Grove cells
- - Large induction coil for producing sparks. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- Induction coil. After Dubois-Reymond, by Krüger, Berlin
- - Electro-magnetic machine. By Smith, New York
- - Small induction coil, with handles. By Elbs, Freiburg
- - Large electro-magnet. Made in the Laboratory
- - Rheochords. By Elbs, Freiburg; by Krille, Leipzig, etc.
- - Galvanometer, with mirror, etc. After Nobili, by Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Compass galvanometer
- - Commutator for four currents. By Marie, Boston
- - Two rocking mercury commutators. By Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Large set of electrodes, electrical connections, and wires (copper, platina, brass, and iron; coarse and flexible; insulated, etc.)
- Surgical, Mechanical, Chemical Outfit
- - Surgical outfit (four pairs scissors, seventeen forceps, seventeen scalpels, fifteen probes, six silver probes, set of saws, scissor-pliers, hammers and chisels for dissecting, set of syringes, camel’s hair brushes, etc.)
- - Glass dissecting slabs
- - Pigeon-holder. After Ewald, by Maier, Strassburg
- - Arrangement for smoking kymograph papers, and fixing the curves in the shellac bath. Made in the Laboratory
- - Carpenter’s bench, with full set of carpenters tools (vice, scrollsaw, etc.)
- - Large grindstone
- - Collection of metal stands and rods, etc.
- - Holder for prisms. By Kohl, Chemnitz
- - Universal holder. By Cambr. Scient. Instr. Co.
- - Glass apparatus (tubes, rods, jars, funnels, etc.)
- - Rubber tubes (from two to twenty-five mm. in diameter), rubber bands, rubber atomizers, etc.
- Porcelain jars, basins, etc.
- - Brass and copper sheets, nails, screws, hooks, pins, corks, straw, wadding, boards, boxes, cloth, linen, etc.
- - Chemical apparatus and reagents
- - Jar of mercury
- - Blast lamp and bellows for glass blowing
- - Bunsen burner
- - Set of soldering tools
- - Water-motor
- - Edison mimeograph, copying-machine